Nutritional Composition of Tortilla Chips
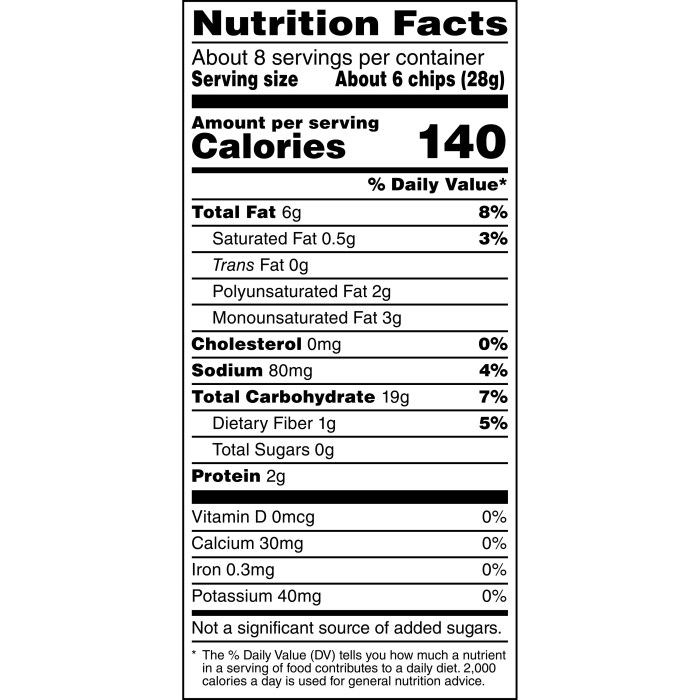
Tortilla chips nutrition facts – The seemingly simple tortilla chip holds a surprisingly complex nutritional profile, varying wildly depending on its ingredients and processing. Understanding this profile is crucial for making informed dietary choices, especially given their widespread consumption as a snack or culinary component. This section delves into the macronutrient and micronutrient composition of various tortilla chip types, highlighting the differences and potential health implications.
Macronutrient Breakdown in Tortilla Chips
A typical serving of tortilla chips (approximately 1 ounce or 28 grams) is predominantly composed of carbohydrates, with a significant portion being complex carbohydrates from the corn or wheat. Protein content is relatively low, while fat content can vary considerably based on the type of chip and added oils. Fiber, crucial for digestive health, is also present, although the amount differs significantly between corn, wheat, and multigrain varieties.
For instance, a serving of corn tortilla chips might contain around 14 grams of carbohydrates, 1 gram of protein, and 8 grams of fat, with approximately 1 gram of fiber. These values are estimates and can change depending on the brand and specific recipe.
Micronutrient Profile of Tortilla Chips
While not a primary source of vitamins and minerals, tortilla chips do contribute small amounts of certain micronutrients. These typically include small quantities of B vitamins (like niacin and thiamin) and minerals such as iron. However, the amounts are generally modest, and reliance on tortilla chips as a significant source of these nutrients is not advisable. For example, a serving might contain trace amounts of iron, less than 1% of the recommended daily intake.
The micronutrient content is also affected by the type of grain used and any added enrichments.
Tortilla chips, those crispy, salty companions to so many dips, often boast a hefty dose of carbohydrates and sodium. For a healthier counterpoint, consider the nutritional profile of something like fage plain yogurt 5 nutrition facts , which offers protein and calcium. Returning to our crunchy friends, remember that moderation is key when enjoying the salty satisfaction of tortilla chips.
Nutritional Differences Between Tortilla Chip Types, Tortilla chips nutrition facts
Corn, wheat, and multigrain tortilla chips exhibit noticeable differences in their nutritional profiles. Corn tortilla chips, typically made from whole corn, tend to be lower in fat and higher in fiber compared to wheat tortilla chips. Wheat tortilla chips, often made from refined wheat flour, generally have a higher carbohydrate content and lower fiber. Multigrain tortilla chips, incorporating various grains, aim to offer a more balanced nutritional profile, often boasting increased fiber and potentially more micronutrients.
However, the sodium content can be significantly higher across all types, largely due to added salt during processing. Excessive sodium intake is linked to several health concerns, prompting careful consideration of portion size.
Comparative Nutritional Information of Tortilla Chips
| Nutrient | Corn Tortilla Chips (per serving) | Wheat Tortilla Chips (per serving) | Multigrain Tortilla Chips (per serving) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 140-160 | 150-170 | 130-150 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 18-20 | 20-22 | 16-18 |
| Fiber (g) | 2-3 | 1-2 | 3-4 |
| Protein (g) | 2-3 | 2-3 | 2-4 |
| Fat (g) | 8-10 | 9-11 | 7-9 |
| Sodium (mg) | 150-200 | 160-210 | 140-190 |
Health Considerations and Serving Suggestions

Tortilla chips, a ubiquitous snack, offer a satisfying crunch and versatility, but their frequent consumption can lead to unforeseen health consequences. Understanding these potential downsides and adopting mindful eating habits is crucial for enjoying this popular treat without compromising well-being. The seemingly innocuous crunch can, in excess, contribute significantly to an unhealthy dietary pattern.The allure of tortilla chips lies in their salty, savory flavor and satisfying texture.
However, this very appeal often masks their high caloric density and substantial sodium content. Excessive consumption can readily lead to weight gain, particularly if paired with high-fat dips like sour cream or cheese. Furthermore, the high sodium content can contribute to elevated blood pressure, a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease. The sheer volume of chips easily consumed in a single sitting, often without conscious awareness of portion size, exacerbates these risks.
This is particularly relevant given the ease with which one can finish an entire bag, a quantity far exceeding recommended serving sizes.
Portion Control and Mindful Consumption
Strategies for controlling portions and fostering mindful eating habits are essential for mitigating the potential negative health impacts of tortilla chip consumption. A simple approach involves pre-portioning chips into smaller, individual serving bags or containers before consumption. This visual cue can significantly influence the quantity consumed. Another helpful technique is to actively pay attention to hunger and fullness cues, consciously slowing down the eating process, and savoring each bite.
This deliberate approach contrasts with the often mindless consumption that accompanies watching television or engaging in other distracting activities. By consciously choosing smaller servings and paying attention to bodily signals, individuals can better regulate their intake and minimize potential health risks.
Creative and Healthy Incorporation into Meals
Tortilla chips, when consumed thoughtfully, can be incorporated into meals and snacks in ways that enhance their nutritional profile and reduce the risk of overconsumption. Crushing them into a coarse crumble adds satisfying texture and subtle flavor to salads, offering a welcome alternative to croutons. They can also serve as a crispy topping for soups, adding a delightful crunch to otherwise creamy or brothy dishes.
Their versatility extends to dips, where a small portion can be enjoyed alongside fresh salsas, guacamole, or black bean dips, all of which offer valuable vitamins, minerals, and fiber. This approach promotes a balanced and more nutritious snack or meal.
Nutritional Information of a Healthy Snack
Imagine a small bowl, perhaps a ramekin, holding a modest serving (approximately 1 ounce, or about 15-20 chips) of baked tortilla chips. Nestled alongside are vibrant scoops of chunky guacamole, its avocado green punctuated by flecks of red onion and cilantro. A small dollop of fresh pico de gallo, a colorful medley of diced tomatoes, onions, jalapeños, and cilantro, adds a refreshing tang.
This snack offers a balanced blend of healthy fats from the avocado, fiber from the chips and vegetables, and a modest amount of sodium. While the exact nutritional breakdown varies based on the specific brands and ingredients used, this combination provides a satisfying and relatively healthy alternative to a larger serving of chips alone. The image is one of vibrant colors and textures, a visual representation of a balanced and mindful approach to snacking.
The rustic simplicity of the bowl, perhaps ceramic, emphasizes the focus on the fresh ingredients, not just the chips. The overall effect is less about indulgence and more about conscious enjoyment of a nutritious snack.
Ingredients and Additives

The seemingly simple tortilla chip belies a complex interplay of ingredients and additives, a silent narrative etched into its crisp, salty surface. Understanding these components is crucial to appreciating the nutritional landscape and potential health implications of this ubiquitous snack. The journey from humble corn to crunchy chip involves a carefully orchestrated process, one that often introduces elements beyond the core ingredients.The foundation of most tortilla chips is, unsurprisingly, corn.
Specifically, it’s typically corn flour or masa harina, a nixtamalized corn flour which gives the chips their characteristic texture and flavor. Oil, usually vegetable oil (such as sunflower, soybean, or canola), is essential for frying, contributing to the chip’s satisfying crispness. Salt, a ubiquitous seasoning, enhances the overall taste profile. Beyond these basics, however, lies a world of additives, some beneficial, others potentially problematic.
Types and Effects of Additives in Tortilla Chips
Additives in tortilla chips serve a variety of purposes, from extending shelf life to enhancing flavor and appearance. Preservatives, such as BHA (butylated hydroxyanisole) and BHT (butylated hydroxytoluene), are commonly used to prevent rancidity and extend the product’s shelf life. Artificial colors, like Yellow 5 and Yellow 6, may be added to enhance the visual appeal of the chips, giving them a more consistent golden hue.
Artificial flavors are employed to create or amplify specific taste notes, often mimicking the subtle nuances of freshly cooked corn.The impact of these additives on health is a subject of ongoing debate. While generally considered safe in the amounts typically used, some studies have linked certain artificial colors and preservatives to potential hyperactivity in children and other adverse health effects.
However, the evidence is often inconclusive and requires further research to establish definitive cause-and-effect relationships. The levels of these additives are regulated by food safety agencies, aiming to minimize potential risks.
Comparative Analysis of Brand Ingredients
A simple comparison of ingredient lists across different tortilla chip brands reveals significant variations. Some brands pride themselves on using only natural ingredients, eschewing artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives. Their ingredient lists might be remarkably short, featuring only corn, oil, and salt. In contrast, other brands may include a longer list, with various additives clearly identified. These differences often reflect different manufacturing processes, target markets, and brand philosophies.
For example, a “health-conscious” brand might prioritize organic corn and extra virgin olive oil, resulting in a higher price point but potentially a healthier profile. A mass-market brand, on the other hand, might prioritize cost-effectiveness, leading to the inclusion of less expensive oils and a greater reliance on additives. The nutritional information panel, which details fat, carbohydrate, protein, and sodium content, also varies significantly across brands, underscoring the importance of careful label reading.
Potential Health Effects of Common Additives
The following list Artikels potential health effects associated with some common additives found in tortilla chips. It is important to remember that the effects are often dose-dependent and the research is ongoing. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
- Butylated Hydroxyanisole (BHA) and Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT): These preservatives have been linked to potential hormonal disruption and increased cancer risk in some animal studies, though human studies have yielded mixed results.
- Artificial Colors (e.g., Yellow 5, Yellow 6): Some studies suggest a potential link between certain artificial colors and hyperactivity in children, although the evidence remains inconclusive.
- Artificial Flavors: The potential health effects of artificial flavors vary widely depending on the specific compound. Some artificial flavors might contain substances that some individuals are sensitive to, causing allergic reactions or other adverse effects. The long-term effects of many artificial flavors are not fully understood.
- High Sodium Content: Excessive sodium intake is linked to high blood pressure, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- High Fat Content: Consuming a diet high in unhealthy fats (saturated and trans fats) is associated with increased risk of heart disease and other health problems.
FAQ Overview: Tortilla Chips Nutrition Facts
Are baked tortilla chips healthier than fried ones?
Generally, yes. Baked tortilla chips typically contain less fat and fewer calories than fried ones.
What are some healthy ways to eat tortilla chips?
Pair them with salsa, guacamole, or black bean dip for added nutrients and fiber. Use them as a crunchy topping for salads or soups.
Are there gluten-free tortilla chips?
Yes, corn tortilla chips are naturally gluten-free. Always check the label to ensure there’s no cross-contamination.
How much sodium is typically in a serving of tortilla chips?
Sodium content varies greatly depending on the brand and type. Always check the nutrition label for specific information.
Can I make my own tortilla chips at home?
Absolutely! It’s a great way to control the ingredients and reduce sodium and unhealthy fats.
